Cancer is a disease of cells in which they divide and grow in an uncontrolled and disorderly manner to form a lump called tumour which if left untreated spreads to surrounding tissues and distant organs. When the cancer arises in ovaries it is called ovarian cancer. Overall 1 in 50 (2%) women get ovarian cancer worldwide. Annually 26834 women are diagnosed of the cancer and 19549 (72%) women die in India.
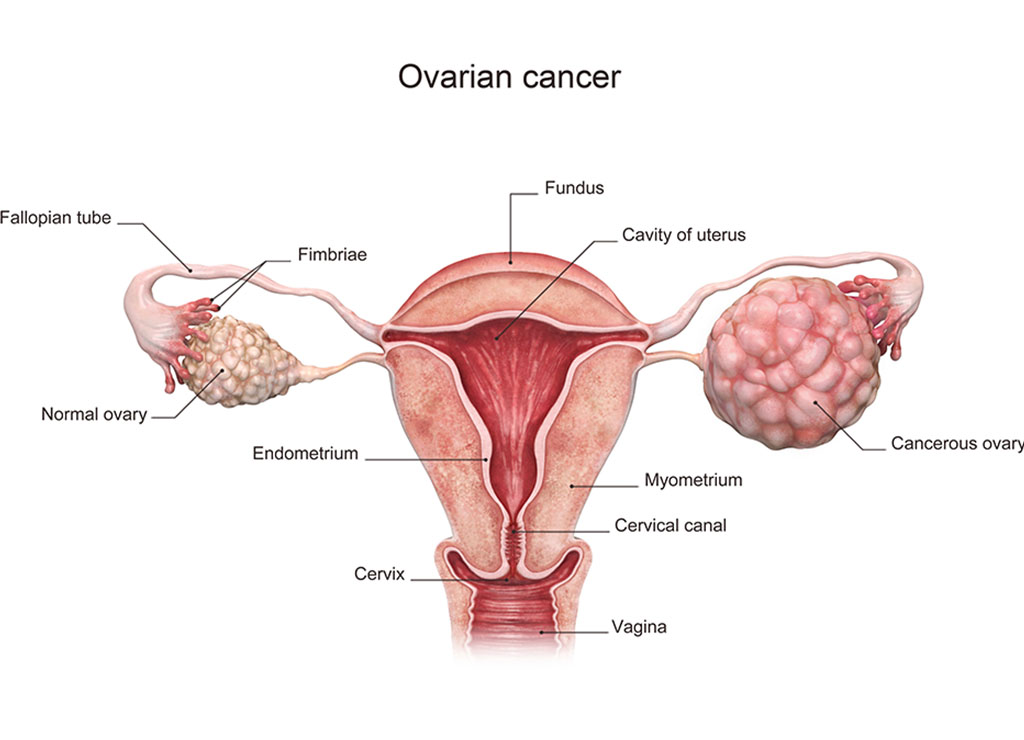
The causes of Ovarian cancer are not completely understood. The risk factors include:
Age: More than 80% of ovarian cancers arise in women above 55 years after the age of menopause.
Hormonal factors: early periods, late menopause, taking Hormones for fertility/ as hormone replacement therapy
Physical factors: Endometriosis, Ovarian cysts
Lifestyle factors: Smoking, Obesity , Diet rich in animal fat
Family history : 2 or more relatives(paternal or maternal) having ovarian, breast, colon and uterine cancer increases the risk to 5%
Inherited risk : A small number of cancers 10% are due to inherited altered gene (genetic mutation) BRCA1 and BRCA 2.
Symptoms caused by ovarian cancer can be similar to symptoms caused by other common conditions such as
Because the symptoms of ovarian cancer can be mistaken for symptoms of other non cancerous conditions, there usually is a delay in diagnosis . Most ovarian cancers (75%) are diagnosed in advanced stage making it more difficult to treat . Therefore ovarian cancer has the lowest 5 -year survival amongst all the gynaecological cancers around 45% which has remained unchanged over last 2 decades.
To help make sure that women with cancer are diagnosed as early as possible , it is recommended that women who have the above symptoms lasting for a month or occurring 12-15 days every month should see a specialist consultant for tests
There is no routine, simple test to accurately detect ovarian cancer. Also there is no accurate and reliable screening test for ovarian cancer.
The tests commonly used in the diagnosis are :
There are 2 risk reducing strategies:
Factors that increase the risk of endometrial cancer include:
Birth control pill: Oral contraceptives have been shown to reduce the risk for ovarian cancer by up to 30-60%.
Preventive surgery to remove the ovaries and fallopian tubes.may be considered if genetic testing indicates an increased risk of ovarian cancer.
For post-menopausal women, this surgery can reduce the risk of ovarian and related cancers by 85-90%.
For premenopausal women, removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes can also reduce the risk of breast cancer by 40-70%.
Research has shown that the most common and most serious form of ovarian cancer actually starts in the fallopian tubes. Any woman seeking gynecologic surgery may wish to discuss having her fallopian tubes removed at that time.
Maintaining a healthy body weight may also reduce risk: It is important to consider the range of risks and benefits when making these important decisions. Your doctor should be able to discuss these with you.
Most ovarian cancers start on the surface of ovary and are called epithelial ovarian cancers and can be serous, mucinous, endometriod, clear cell type. All types are treated similarly
Grading depends on how cancer cells look under the microscope and are borderline, low grade, moderate, or high grade. The stage of cancer is a term used to describe its size and spread . it is often not possible to tell exactly the stage of ovarian cancer until an operation is done. Staging and grading help in deciding the treatment plan.
The main treatments for ovarian cancer include Surgery and Chemotherapy . Other treatments used are Targeted therapy , Radiotherapy
The standard surgery -Removal of ovaries , tubes and the womb and omentum(fatty layer covering the bowel), removal of lymph nodes is called TAH+ BSO +omentectomy + lymphadenectomy aims to remove all of the cancer .
When cancer has spread to other areas in abdomen , aim is to try and remove as much cancer as possible safely. This is called debulking. This may also involve removing some of the bowel and joining the remaining pieces of bowel. Rarely bowel cant be rejoined and upper end of the bowel is brought out onto the skin by a stoma and a bag is worn over it to collect the stools.
In some women with early cancer it may be possible to remove just the affected tube and ovary and take biopsies of other tissues. If the results of the biopsies suggests that there is no spread beyond the ovary , they may be able to get pregnant in future. However if the biopsies show spread then they have to undergo a second operation to remove the other ovary and tube.
Chemotherapy uses anti- cancer drugs to destroy cancer cells. Ovarian cancer is usually very sensitive to chemotherapy . Chemotherapy drugs are usually given into a vein(Intravenously). It is given as a session over several hours followed by a rest period for a few weeks called a cycle. Most women have six cycles of chemotherapy. Most commonly chemotherapy is given after surgery to treat any remaining and complete course lasts for 4-5 months. Sometimes chemotherapy maybe given both before and after surgery : to make surgery more successful. Sometimes it is given as the main treatment when cancer is spread to liver and abdomen.
Women need to have regular check ups and CA-125 tests to see if the cancer is coming back (recurrence) . Symptoms of recurrence are bowel problems, indigestion, pain or bloating , weight loss and extreme tiredness.
Copyright ©2021 Dr. Vrunda Karanjgaokar