Endometrial cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the uterus. The uterus is the hollow, pear-shaped pelvic organ in women where fetal development occurs. Endometrial cancer begins in the layer of cells that form the lining (endometrium) of the uterus. Endometrial cancer is sometimes called uterine cancer.
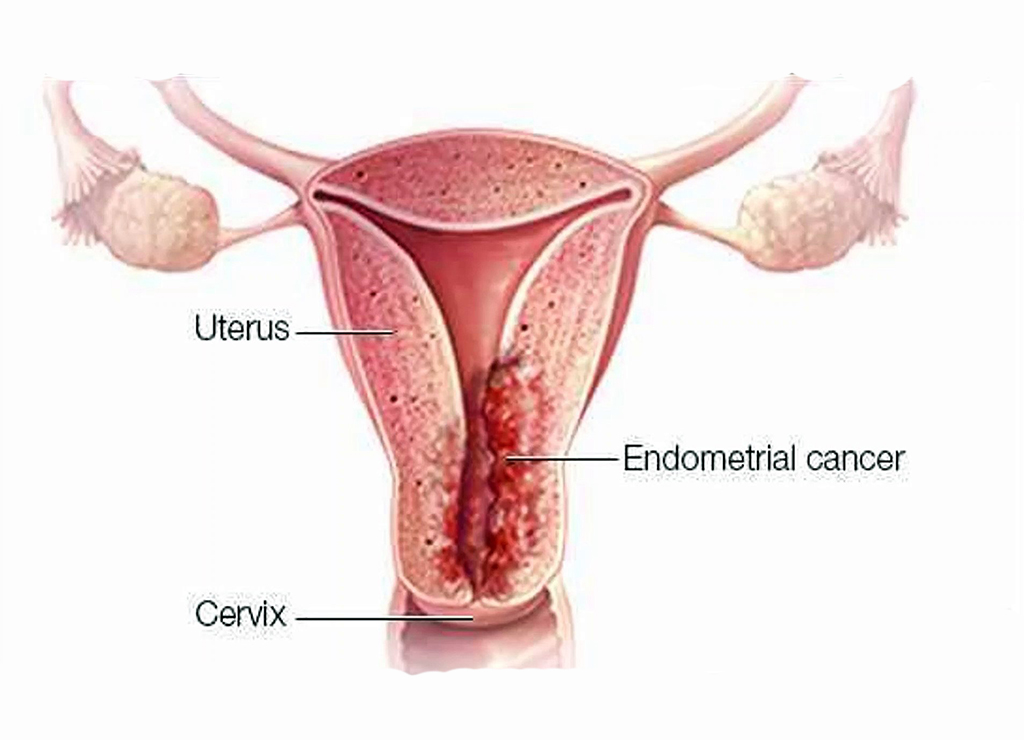
Other types of cancer can form in the uterus, including uterine sarcoma, but they are much less common than endometrial cancer. Endometrial cancer is often detected at an early stage because it frequently produces abnormal vaginal bleeding, which prompts women to see their doctors. If endometrial cancer is discovered early, removing the uterus surgically often cures endometrial cancer.
Signs and symptoms of endometrial cancer may include:
Make an appointment with us if you experience any signs or symptoms that worry you, such as vaginal bleeding or discharge not related to your periods, pelvic pain, or pain during intercourse.
We don't know exactly what causes endometrial cancer. What's known is that something occurs to create a change within cells in the endometrium — the lining of the uterus.
The change turns normal, healthy cells into abnormal cells. Healthy cells grow and multiply at a set rate, eventually dying at a set time. Abnormal cells grow and multiply out of control, and they don't die at a set time. The accumulating abnormal cells form a mass (tumor). Cancer cells invade nearby tissues and can separate from an initial tumor to spread elsewhere in the body (metastasize).
Factors that increase the risk of endometrial cancer include:
Changes in the balance of female hormones in the body. Your ovaries make two main female hormones — estrogen and progesterone. Fluctuations in the balance of these hormones cause changes in your endometrium.
A disease or condition that increases the amount of estrogen, but not the level of progesterone, in your body can increase your risk of endometrial cancer. Examples include irregular ovulation patterns, such as those that can occur in women with polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity and diabetes. Taking hormones after menopause that contain estrogen but not progesterone increases the risk of endometrial cancer.
A rare type of ovarian tumor that secretes estrogen also can increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
More years of menstruation. Starting menstruation at an early age — before age 12 — or beginning menopause later increases the risk of endometrial cancer. The more periods you've had, the more exposure your endometrium has had to estrogen.
Never having been pregnant. Women who have never been pregnant have a higher risk of endometrial cancer than do women who have had at least one pregnancy.
Older age. As you get older, your risk of endometrial cancer increases. Endometrial cancer occurs most often in women who have undergone menopause.
Obesity. Being obese increases your risk of endometrial cancer. This may occur because excess body fat alters your body's balance of hormones.
Hormone therapy for breast cancer. Women with breast cancer who take the hormone therapy drug tamoxifen have an increased risk of developing endometrial cancer. If you're taking tamoxifen, discuss this risk with your doctor. For most women, the benefits of tamoxifen outweigh the small risk of endometrial cancer.
An inherited colon cancer syndrome. Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) is a syndrome that increases the risk of colon cancer and other cancers, including endometrial cancer. HNPCC occurs because of a gene mutation passed from parents to children. If a family member has been diagnosed with HNPCC, discuss your risk of the genetic syndrome with your doctor. If you've been diagnosed with HNPCC, ask your doctor what cancer screening tests you should undergo
Copyright ©2021 Dr. Vrunda Karanjgaokar