Cervical cancer is the cancer of cervix- the entrance of the womb from the vagina Cervical cancer is of different types depending on the type of cell affected . The most common is squamous cell carcinoma (80%), Adenocarcinoma (20%) ,Adenosquamous carcinoma , Clear-cell and Small-cell carcinomas. Globally it is the third most common cancer in women, and the seventh overall with estimated 530 000 new cases/year*.
More than 85% of the global burden occurs in developing countries, where it accounts for 13% of all female cancers. There are approximately 1400 new cases in Mumbai annually. The Incidence: Mortality Ratio for cervical cancer -52% in India ie: more than 52% women affected by cervical cancer in India.
Who gets cervical cancer ? Persistent infection with HPV is the main cause of cervical cancer (99.7% of cases). HPV is transmitted through sexual contact , therefore all sexually active women are susceptible.
It is not hereditary .It occurs most often in women over age 30 yrs. Women who have sex early in life, have multiple sex partners, who smoke, or have HIV and are on immunosuppresants are at increased risk for cervical cancer
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is a common virus affects skin and mucosa. There are more than 100 different types of HPV of which 20 strains cause cancer.
HPV 16 and HPV 18 are responsible for 70% of all cases of cervical cancer . 80% of the sexually active women will have HPV infection at some point in their life. However HPV infection can be asymptomatic. Infection with HPV does NOT imply either infidelity or promiscuity
Symptoms of Cervical cancer include abnormal vaginal bleeding commonly bleeding after sex, foul smelling vaginal discharge , discomfort during sex. It advisable that women should go to the specialist promptly on presence of these symptoms.
Investigations such as internal examination, blood tests, pap smear, biopsy, and imaging such as sonography and MRI/CT Scan/PET Scan will be done as required. The specialist will review the reports and do further assessments such examination under anaesthesia & cystoscopy. Treatment depends on patient factors such as Age, Fertility Status ie with children, Cell type, Stage of cancer and Medical Fitness .
The intent of Cervical cancer is Curative in early stages and includes Surgery , and when more advanced -Radiation or Chemoradiation. . When cancer is very advanced, intent of treatment is palliative ie aimed at making patient comfortable by treating symptoms such as pain etc. It is now possible to do Fertility-preserving surgery for Early Stages and Robotic Surgery in Cervical cancer without compromising the outcome.
Depending on the final report, a woman may require additional treatment such as radiation. Cancer may comeback ie recur and one should watch out for symptoms such as Unexplained weight loss,Leg swelling,Thigh/buttock pain,Blood-stained vaginal discharge Neck lump, Chest pain/cough. Hence the importance of Follow –up and regular visits to the cancer specialists. Cervical cancer affects life on many levels including emotional, psychosexual, financial Hence the importance of Prevention of Cervical cancer and Screening .
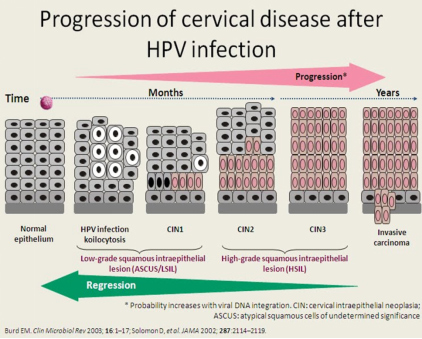
Screening with cytology is a method of examining cells from the cervix to detect pre-cancer (Cervical Intraepithelia Neoplasia). All sexually active women between age 25-64 years should have smears regularly. There are two methods for taking smear the Conventional PAP test or the more recent and accurate Liquid Base Cytology (LBC). Only 5-8% of the smears are abnormal and are graded as- Mild, Moderate and Severe Dyskaryosis. You may be referred for Colposcopy or HPV Test which together with smear can identify 95% of abnormalities.
Colposcopy is an examination where the Colposcopist gets a magnified view of cervix with colposcope and uses solutions such as weak vinegar to highlight abnormal changes. They may take a punch biopsy from abnormal areas if required. If biopsy proves CIN, it can be managed by a small procedure called LLETZ ( Large Loop Excision of Transformation zone). This treatment is 95% successful. Cervical Screening Programme implemented in EU, USA, UK involves healthy women having smears at regular screening intervals . They may differ in the screening interval and age of target population. They are 90% effective when coverage is 80% or more.
HPV vaccination has added a new dimension to the cervical cancer prevention. It has been incorporated in the National vaccination programme of several countries such as UK, USA. Girls between ages of 12- 13 years are vaccinated against HPV 16 and HPV 18 ie before they become sexually active. There are two types of HPV vaccines: Cervarix (bivalent) provides protection against cervical cancer alone and Gardasil (quadrivalent) provides protection against cervical cancer and genital warts .It is recommended as a three-dose course (0,1,6mths) and alone prevents upto 70% of cancers. However it does not replace screening and is expensive
Copyright ©2021 Dr. Vrunda Karanjgaokar